
EOS Labs and EOS Network Foundation (ENF) unveil a strategic collaboration with the EOS Stable Coin Chain (ESCC). This innovative Ethereum-based blockchain operates as a smart contract on the EOS Network, utilizing a tailored implementation of the EOS EVM architecture. The primary goal of this partnership is to elevate the EOS ecosystem by delivering an optimized platform that facilitates high-speed and compliant stablecoin transactions. Through their joint efforts, they will provide a specialized and streamlined solution for managing stablecoins, poised to bring substantial improvements to the EOS ecosystem.
Hiroaki Yamasaki, CEO at ESCC, said, “Collaborating with EOS Labs and the ENF is a significant milestone for ESCC. By being the first blockchain architecture of its kind to use stablecoins as gas fees, we are offering a unique experience to our users, distinct from any other blockchain platform. This innovation is set to transform user interactions within the blockchain space, providing a blend of stability, efficiency, and user-centric design.”
Enhancing Stablecoin Transaction Efficiency
The integration of ESCC into the EOS ecosystem is set to transform the stablecoin transaction arena. Harnessing the high-performance features of EOS EVM technology, this partnership is anticipated to introduce unparalleled transaction efficiency. Essential performance metrics highlight the strides made in this advancement:
Lightning Speed: ESCC achieves swift processing with block intervals of just 1 second, significantly slashing transaction times.
Low Gas Fee: Transaction costs are exceptionally economical, hovering around 0.005 USD per transaction, thereby enhancing the accessibility and cost-effectiveness of stablecoin transactions.
High Throughput: The system exhibits an impressive capacity for high-volume transaction processing, handling over 950 swaps per second. This surpasses the capabilities of other technologies in this regard.
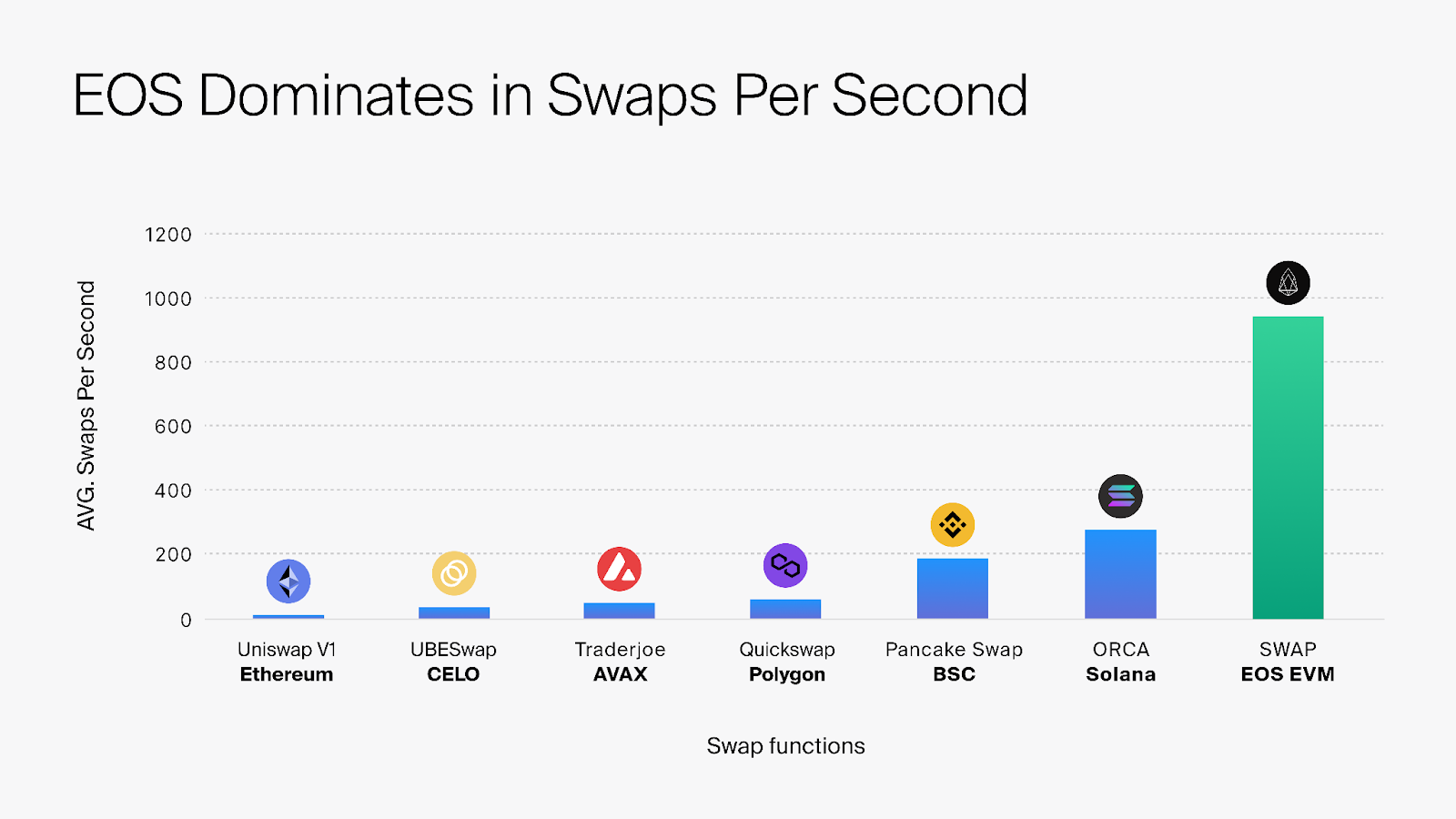
Huaqiang Wen, Founder and CEO of EOS Labs, said, “ESCC serves as a prime illustration of how EOS EVM is extending its reach into enterprise-level ecosystem applications, highlighting the strengths of its technical design. This advancement is pivotal in facilitating the roll-out and execution of more enterprise-oriented applications within the EOS ecosystem.”
Bringing Innovation to Financial Transactions
The partnership among EOS Labs, EOS Network Foundation, and ESCC is poised to harness the state-of-the-art EOS EVM architecture, instigating transformative shifts in financial transactions within the blockchain sphere. A pivotal innovation is encapsulated in ESCC’s pioneering strategy of employing stablecoins for gas fees.
This technical leap forward is facilitated by the seamless integration of EOS EVM, allowing the system to process transactions in a manner familiar to Ethereum developers while optimizing the user experience. By incorporating stablecoins for transaction costs, ESCC significantly improves cost predictability and alleviates the conventional volatility linked to cryptocurrency-based gas fees.
Yves La Rose, Founder and CEO of the EOS Network Foundation, said, “Integrating compliance and adopting stablecoins for transaction fees on ESCC is a pivotal innovation that reshapes how we approach blockchain efficiency and creates new avenues for development. This initiative reflects more than just a boost to our network’s functionality; it underscores our dedication to pioneering new solutions and our agility in responding to the dynamic landscape of the blockchain sector.”
Delivering Customizable Blockchain Solutions
ESCC’s collaboration with the EOS Network capitalizes on its adaptable architecture, catering to both open and regulated stablecoin environments, including sophisticated KYC processes. This aligns seamlessly with the EOS Network’s objective of providing versatile and compliant blockchain solutions.
The flexible framework of ESCC is well-suited for a spectrum of stablecoin applications, spanning from DeFi to regulated financial systems, showcasing its capacity to address diverse industry requirements. This partnership represents a notable stride in delivering scalable and compliant blockchain solutions tailored to various stablecoin use cases.
Streamlining EOS and Ethereum Compatibility
The integration of EOS EVM technology into the ESCC framework stands as a pivotal aspect of this partnership. This integration not only enhances the EOS ecosystem but also effectively bridges the gap with the Ethereum ecosystem. It fosters increased interoperability between the two platforms, empowering developers to utilize Ethereum’s Solidity programming language and existing development tools within the EOS environment.
The compatibility feature of the EOS EVM is particularly advantageous for EVM developers, allowing them to seamlessly migrate and deploy their existing EVM-based applications on ESCC. This initiative opens up new avenues for developer engagement and innovation, leveraging the strengths of both EOS and Ethereum technologies to foster a more inclusive and versatile blockchain ecosystem.
The EOS Network stands as a third-generation blockchain operating system, propelled by a low-latency, highly efficient, and extensible WebAssembly engine designed for the deterministic execution of nearly feeless transactions. It is purpose-built to facilitate optimal Web3 user and developer experiences.
The network incorporates an enterprise-grade Ethereum Virtual Machine embedded within an EOS smart contract, providing feature parity with Ethereum while delivering unparalleled speed, performance, and compatibility. This connection seamlessly links the EOS Network to the Ethereum ecosystem.
In the realm of blockchain, the ESCC distinguishes itself as a tailored solution for stablecoin transactions. By harnessing the high performance of the EOS native system and leveraging the compatibility advantages of the EOS EVM architecture, ESCC is dedicated to the streamlined processing of stablecoin transactions. A pioneering aspect of its methodology involves utilizing stablecoins as gas fees, marking a significant stride in addressing the volatility commonly associated with digital currency transactions.









