Bitcoin (BTC) mining is the backbone of the Bitcoin network—it validates transactions, secures the blockchain, and introduces new bitcoins into circulation. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to mine Bitcoin step by step, covering everything from the basics of mining and necessary hardware to software setup, mining pools, and profitability analysis. Whether you’re a beginner or a crypto enthusiast looking to set up your own mining operation, this comprehensive guide is designed to be your one-stop resource.
Introduction to Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is a critical process that ensures the integrity and security of the Bitcoin blockchain. It involves solving complex mathematical problems using powerful computers to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. As a reward for this work, miners receive newly minted bitcoins and transaction fees.
Mining is not only about earning Bitcoin—it also plays a pivotal role in maintaining the decentralized and trustless nature of the network. By distributing the work of transaction verification among a global network of miners, Bitcoin avoids the pitfalls of centralized control.
How Bitcoin Mining Works
Here is how the process of Bitcoin mining works:
The Proof-of-Work Mechanism
At the heart of Bitcoin mining is the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism. PoW requires miners to compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets the right to add the next block of transactions to the blockchain and is rewarded with a block reward (currently 6.25 BTC, though this reward halves approximately every four years).
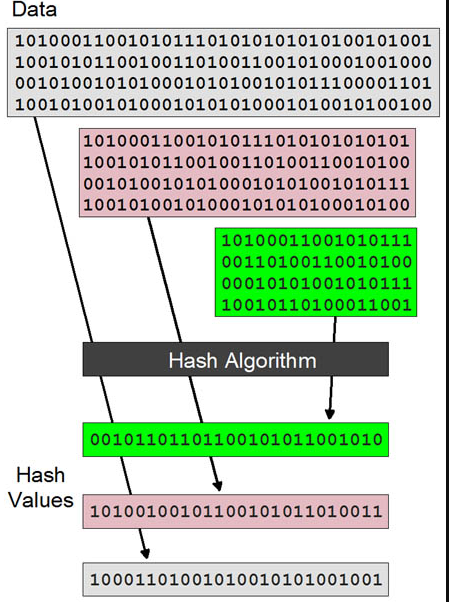
Hash Rate and Mining Difficulty
- Hash Rate: This is the speed at which your mining hardware can solve the cryptographic puzzles, measured in hashes per second (H/s). A higher hash rate increases your chances of solving the puzzle and earning the reward.
- Mining Difficulty: The Bitcoin network automatically adjusts the difficulty of the puzzles approximately every 2,016 blocks (roughly every two weeks) to ensure that a new block is mined roughly every 10 minutes, regardless of the total network hash rate.
The Mining Process
- Transaction Collection: Miners gather transactions from the network and compile them into a block.
- Hashing: Using powerful computer hardware, miners hash the block’s header and attempt to find a hash value below a predetermined target.
- Block Verification: When a miner finds a valid hash, they broadcast the block to the network. Other nodes verify the solution, and if accepted, the block is added to the blockchain.
- Reward Distribution: The successful miner receives the block reward and transaction fees from the transactions within the block.
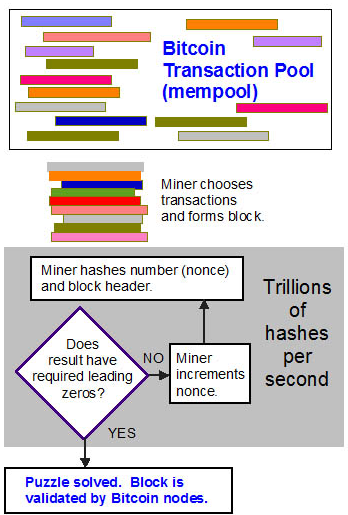
This process not only introduces new bitcoins into circulation but also secures the network by making it computationally expensive to alter past transactions.
Essential Mining Hardware
To mine Bitcoin effectively, you need specialized hardware designed for high-performance computing. The evolution of mining technology has moved from CPUs and GPUs to ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits).
ASIC Miners
ASIC miners are custom-built for mining Bitcoin. They offer:
- High Hash Rates: Significantly faster than GPUs and CPUs.
- Energy Efficiency: Although they consume a lot of power, their efficiency in hashing makes them the preferred choice for serious miners.
- Durability: Designed to run continuously 24/7.
Popular ASIC models include the Bitmain Antminer series (e.g., Antminer S19 Pro) and MicroBT’s Whatsminer. These machines are built exclusively for mining and are optimized for the SHA-256 algorithm that Bitcoin uses.
Other Hardware Considerations
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): A high-quality, efficient PSU is crucial to handle the power consumption of ASIC miners.
- Cooling Systems: Mining generates significant heat. Invest in robust cooling solutions like additional fans or custom cooling setups to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your hardware.
- Mining Rig Setup: For those operating multiple ASICs, consider a dedicated mining rig or facility with proper ventilation, power management, and security measures.
Mining Software and Tools
The right software is as essential as the hardware for a successful mining operation and to understand how to mine Bitcoin. Several mining programs are available that cater specifically to ASIC devices and are designed to optimize performance.
Popular Mining Software
- CGMiner: One of the most popular mining programs, known for its robust features and compatibility with various ASIC miners.
- BFGMiner: Similar to CGMiner, this software offers extensive control over mining operations and supports multiple types of mining hardware.
- ASIC-specific Software: Many ASIC manufacturers provide their own proprietary mining software tailored to their devices.
Setting Up and Configuring Mining Software
- Download and Install: Obtain the mining software from a reputable source.
- Configuration: Configure the software by entering your mining pool details (if you choose to join a pool), wallet address, and device-specific settings such as hash rate limits.
- Monitoring Tools: Utilize built-in monitoring features or third-party tools to keep track of temperature, hash rate, and overall performance. Monitoring ensures that your hardware is functioning optimally and helps detect potential issues early.
Mining Pools vs. Solo Mining
The following is the difference between mining pools and solo mining:
Solo Mining
Solo mining involves mining on your own without joining a pool. While the reward is entirely yours when you solve a block, the probability of successfully mining a block on your own is extremely low unless you have an enormous hash rate. Solo mining can be appealing for those with significant hardware investments and low operational costs, but it’s often not practical for most individual miners.
Mining Pools
Mining pools allow multiple miners to combine their hash power, increasing the overall chance of mining a block. When a block is successfully mined, the reward is distributed among pool members according to the amount of hash power they contributed. Popular mining pools include Slush Pool, F2Pool, and Antpool.
Benefits of Mining Pools:
- Steady Income: Regular, smaller payouts instead of rare, large rewards.
- Lower Variance: The risk of going long periods without earning any reward is mitigated.
- Community and Support: Pools often provide dashboards, support channels, and analytics tools.
Evaluating Bitcoin Mining Profitability
Before investing in mining hardware and infrastructure, it’s crucial to understand the factors that affect profitability. It also helps to better understand how to mine Bitcoin.
Key Factors Influencing Profitability
- Initial Hardware Investment: ASIC miners and supporting hardware can be expensive. Calculate the total cost of acquisition and setup.
- Electricity Costs: Power consumption is one of the biggest ongoing expenses. Miners should aim to operate in regions with low electricity rates.
- Mining Difficulty and Hash Rate: As more miners join the network, mining difficulty increases, which can reduce individual earnings.
- Bitcoin Price Volatility: The value of Bitcoin fluctuates, impacting mining profitability. A drop in price can significantly affect your return on investment (ROI).
- Operational Costs: Consider maintenance, cooling, and potential downtime as part of your overall expenses.
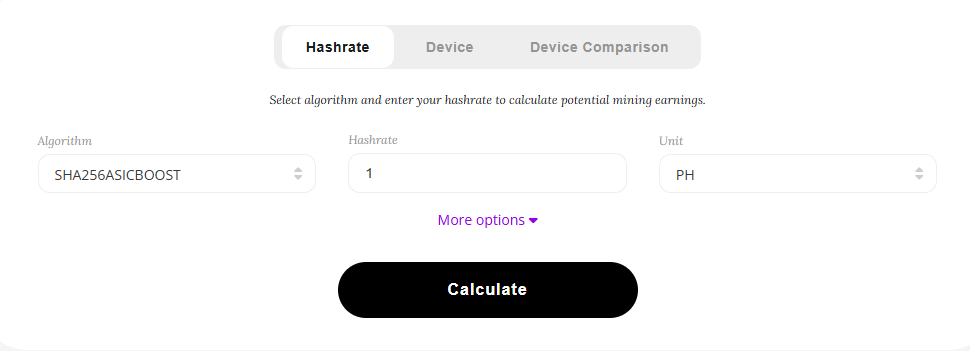
Profitability Calculators
Online mining profitability calculators can help estimate earnings based on hash rate, electricity cost, hardware cost, and current mining difficulty. These tools are invaluable for planning and decision-making.
Setting Up Your Bitcoin Mining Rig
Here is how you can easily set up your Bitcoin mining rig:
Step-by-Step Setup Process
- Procure Your Hardware: Purchase your ASIC miners, power supplies, and cooling equipment.
- Configure Your Workspace: Set up your mining rig in a well-ventilated, secure area with a stable power supply.
- Install the Mining Software: Download and install your chosen mining software on a dedicated computer or mining rig controller.
- Connect Your ASICs: Attach your ASIC devices to your rig and connect them to your network.
- Join a Mining Pool: If opting for pool mining, sign up for a reputable pool and configure your mining software with the pool’s server details and your wallet address.
- Monitor and Optimize: Use software dashboards to monitor performance metrics like hash rate and temperature. Adjust configurations to optimize efficiency and ensure that your equipment is operating within safe parameters.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Overheating: Ensure that your rig is properly cooled. Overheating can lead to reduced performance or hardware damage.
- Connectivity Issues: Maintain a stable internet connection to avoid downtime.
- Software Configuration: Double-check that all settings, including pool details and wallet addresses, are correctly configured.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to setting up a robust Bitcoin mining operation.
Best Practices and Tips for Successful Mining
The following are the best practices and tips to run a successful Bitcoin mining process:
1. Maintain Your Equipment
Regular maintenance is crucial. Dust off your hardware, check for firmware updates, and replace faulty components promptly to ensure maximum efficiency and longevity.
2. Optimize Energy Consumption
Energy efficiency is key to profitability. Consider the following:
- Monitor Power Usage: Use smart plugs or dedicated monitoring tools.
- Optimize Cooling: Invest in high-efficiency fans or consider alternative cooling methods to reduce power consumption.
3. Stay Informed
The cryptocurrency landscape is rapidly evolving. Keep up with the latest news, changes in mining difficulty, and fluctuations in Bitcoin’s price to adjust your strategy accordingly.
4. Secure Your Investment
- Protect Your Wallet: Use hardware wallets and strong security practices to safeguard your earnings.
- Network Security: Secure your mining rig and network against potential cyber threats.
5. Community Engagement
Engage with online forums, mining communities, and social media channels. Sharing experiences and solutions with fellow miners can provide valuable insights and support.
Conclusion
The process of how to mine Bitcoin is both an art and a science—one that requires significant investment in hardware, a deep understanding of blockchain technology, and continuous adaptation to a dynamic market environment. In this guide, we explored the fundamentals of Bitcoin mining, from how the proof-of-work mechanism operates and the importance of hash rates to the detailed process of setting up mining hardware and joining mining pools.
We also discussed the economic factors that influence mining profitability, emphasizing the need to consider electricity costs, hardware investments, and market volatility. Whether you choose to mine solo or join a mining pool, understanding these dynamics is essential for maximizing your return on investment.
Happy mining, and may your hash rate be high and your energy costs low!








