- Introduction
- Understanding Blockchain Data-Sharing
- The Role of Distributed Ledger Technology
- Consensus Mechanisms for Data-Sharing
- Transparency and Decentralization in Data-Sharing
- Smart Contracts and Data-Sharing
- Data Privacy and Security
- Different Types of Blockchains for Data-Sharing
- Final Words
- FAQ
Introduction
Blockchain technology has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to revolutionize various industries. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger that ensures transparency, immutability, and security of data. One key aspect of blockchain is its ability to facilitate data-sharing among participants in a decentralized network. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of data-sharing in a blockchain and analyze different statements describing this process.
Understanding Blockchain Data-Sharing
Blockchain technology enables data-sharing through its distributed ledger. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where data is stored in a single location, a blockchain network consists of multiple nodes that maintain a copy of the ledger. This distributed nature ensures transparency and immutability, making it ideal for sharing data in a trustless environment. Which statement describes data-sharing in a blockchain? Let’s explore further.

The Role of Distributed Ledger Technology
The distributed ledger in a blockchain acts as a shared database, recording transactions and storing data. It maintains a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. These transactions can include data that is shared among network participants. The use of cryptography ensures the security and integrity of the shared data. Within this context, it is important to understand which statement describes data-sharing in a blockchain accurately.
Consensus Mechanisms for Data-Sharing
Consensus mechanisms play a crucial role in validating and agreeing upon shared data in a blockchain network. Various consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS), and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), ensure agreement among participants on the validity of transactions and shared data.
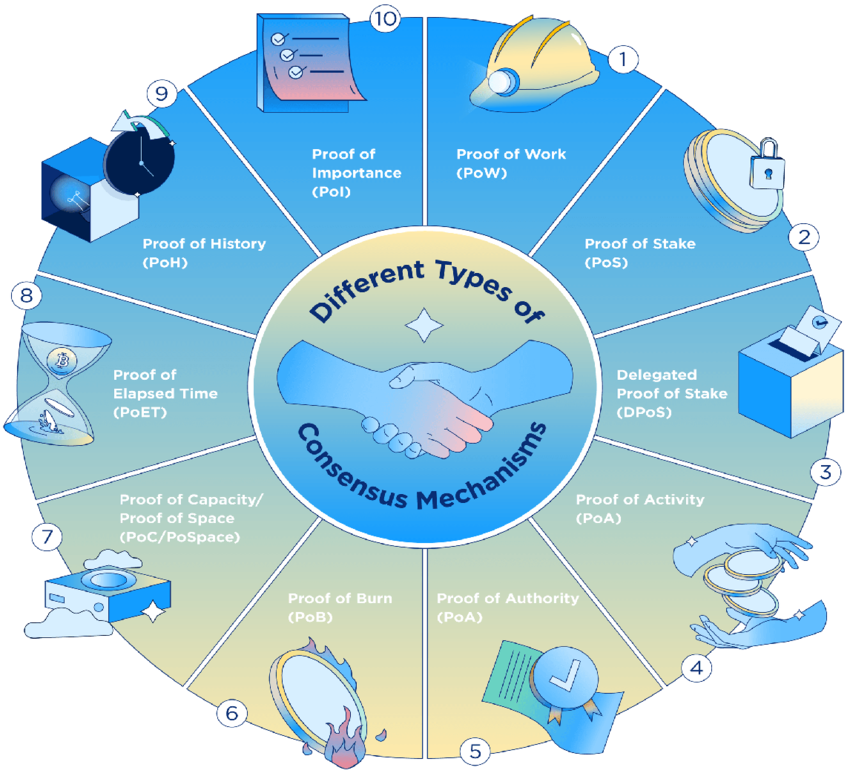
Transparency and Decentralization in Data-Sharing
Transparency is a fundamental characteristic of blockchain technology. All participants in the network can view and verify the shared data, promoting trust and accountability. Decentralization ensures that no single entity has control over the data, reducing the risk of manipulation or censorship.
Smart Contracts and Data-Sharing
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements coded on the blockchain. They facilitate automated and secure data-sharing by defining the conditions under which data can be accessed, modified, or transferred. Smart contracts enable parties to share data without relying on intermediaries, streamlining processes and reducing costs.

Data Privacy and Security
Blockchain technology provides a unique approach to data privacy and security. While blockchain transactions are transparent, the identity of the participants involved can remain pseudonymous. Additionally, cryptography ensures the confidentiality and integrity of shared data, making it tamper-resistant and secure.
Different Types of Blockchains for Data-Sharing
Blockchain networks can be categorized into permissioned and permissionless, public and private. Permissioned blockchains restrict access to data-sharing among authorized participants, ensuring greater control and privacy.
- Permissioned blockchains provide a controlled environment for data-sharing, where participants must obtain authorization to join the network. This enhances data security and allows for greater control over access and permissions. Immutable records ensure that once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, maintaining the integrity of shared information.
- In contrast, permissionless blockchains, such as public blockchains, allow anyone to participate in the network and share data. These networks operate on a peer-to-peer basis, where participants directly interact with each other without the need for intermediaries. The decentralized nature of a peer-to-peer network ensures that no single entity has control over the data-sharing process.
- Data validation is an essential aspect of data-sharing in a blockchain. Consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), verify the accuracy and validity of shared data. Through consensus, blockchain networks ensure that only verified and legitimate data is added to the ledger.
- Data ownership is an important consideration in blockchain data-sharing. In a blockchain network, participants have ownership of their data and can choose how and with whom to share it. Smart contracts play a crucial role in governing data ownership rights and permissions, allowing individuals or organizations to retain control over their data.
- Data provenance refers to the origin and history of shared data. Blockchain’s transparent and immutable nature allows participants to trace the history of data, verifying its authenticity and ensuring its reliability. This feature is particularly valuable in industries such as supply chain management, where tracking the origin and movement of goods is critical.
- Blockchain data-sharing protocols and mechanisms define the rules and processes for sharing data in a blockchain network. These protocols determine how data is exchanged, validated, and stored on the blockchain. They establish the framework for secure and efficient data-sharing, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of shared information.
- Distributed ledger technology and data sharing go hand in hand. The distributed nature of a blockchain ensures that multiple copies of the ledger are maintained across the network, increasing data redundancy and resilience. This eliminates the need for a central authority and reduces the risk of data loss or manipulation.
- Data-sharing models in blockchain networks vary based on the specific use case and requirements. Different industries and applications may adopt different approaches to data-sharing, depending on factors such as privacy, security, and scalability. Blockchain data exchange methods can include direct peer-to-peer sharing, data access through smart contracts, or through specialized protocols and APIs.
- Secure data-sharing in blockchain systems is achieved through the implementation of cryptographic techniques. Encryption algorithms protect the confidentiality of shared data, ensuring that only authorized parties can access and decrypt it. Additionally, blockchain’s immutability and consensus mechanisms enhance data security, making it highly resistant to tampering or unauthorized modifications.
- Trust and transparency are core principles of blockchain data-sharing. By eliminating the need for intermediaries and relying on consensus algorithms, blockchain networks foster trust among participants. The transparent nature of blockchain allows participants to independently verify the integrity and authenticity of shared data, promoting transparency and accountability.
- Data integrity is a critical aspect of blockchain data-sharing. Through the use of cryptographic hash functions, blockchain ensures that shared data remains unchanged and tamper-proof. Each transaction and block in the blockchain is linked to the previous one, creating a chain of data that can be audited and verified for integrity.
- Scalability and efficiency are key considerations in blockchain data-sharing. As blockchain networks grow and more data is shared, scalability becomes crucial to ensure smooth and timely processing of transactions. Various solutions, such as sharding, sidechains, or layer-two protocols, aim to address scalability challenges while maintaining the efficiency of data-sharing processes.
- Data governance in blockchain data-sharing is essential to establish rules, policies, and standards for the management and control of shared data. It involves defining roles and responsibilities, specifying data access permissions, and implementing mechanisms for data quality assurance and compliance.
- Interoperability is an important aspect of blockchain data-sharing, especially in multi-blockchain or hybrid environments. Interoperability allows different blockchain networks to communicate and share data seamlessly. Standards, protocols, and interoperability frameworks enable the exchange of data across different blockchain platforms, enhancing collaboration and expanding the possibilities of data-sharing.
- Regulatory considerations play a significant role in blockchain data-sharing. Depending on the jurisdiction and industry, there may be legal and regulatory requirements that impact how data can be shared on a blockchain. Compliance with data protection, privacy, and industry-specific regulations is essential to ensure that data-sharing practices align with legal obligations and ethical standards.
- Auditing and accountability mechanisms are integral to blockchain data-sharing. The transparent and immutable nature of blockchain enables effective auditing of shared data, allowing for independent verification and validation. Accountability measures, such as identity management and reputation systems, can be implemented to hold participants responsible for their actions and ensure the integrity of data-sharing processes.
Final Words
In conclusion, data-sharing in a blockchain involves the secure and transparent exchange of information among participants in a decentralized network. With the use of distributed ledger technology, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts, blockchain ensures the integrity, privacy, and ownership of shared data. By leveraging blockchain data-sharing protocols and mechanisms, organizations can establish trust, enhance transparency, and enable efficient collaboration in various industries. However, challenges such as scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance must be addressed to unlock the full potential of blockchain data-sharing. As this technology continues to evolve, further research and innovation will shape the future of data-sharing in blockchain networks.
FAQ
What is data-sharing in a blockchain?
Data-sharing in a blockchain refers to the process of securely and transparently exchanging information among participants in a decentralized network using distributed ledger technology.
Which statement accurately describes data-sharing in a blockchain?
The statement that accurately describes data-sharing in a blockchain depends on various factors such as consensus mechanisms, transparency, smart contracts, data privacy, and security.
How does a blockchain ensure the security of shared data?
Blockchain ensures the security of shared data through cryptographic techniques that protect the confidentiality and integrity of information. The immutability of records and consensus mechanisms further enhance data security.
What are the different types of blockchains for data-sharing?
Blockchains can be categorized as permissioned or permissionless, public or private. Permissioned blockchains restrict access to authorized participants, while permissionless blockchains allow anyone to participate.
How does data ownership work in a blockchain?
In a blockchain, participants have ownership of their data and can determine how and with whom they share it. Smart contracts play a role in governing data ownership rights and permissions.
How is data integrity maintained in blockchain data-sharing?
Data integrity is ensured through the immutability of records in a blockchain. Once data is added, it cannot be altered or deleted, maintaining the integrity and trustworthiness of the shared information.
What are the challenges in data-sharing within blockchain networks?
Challenges in blockchain data-sharing include scalability, efficiency, data governance, interoperability, regulatory compliance, and addressing privacy concerns.
What is the role of smart contracts in data-sharing within a blockchain?
Smart contracts automate and secure data-sharing by defining the conditions under which data can be accessed, modified, or transferred. They eliminate the need for intermediaries and streamline processes.
How does transparency play a role in data-sharing within a blockchain?
Transparency is a fundamental characteristic of blockchain technology. All participants can view and verify shared data, promoting trust, accountability, and facilitating auditing and accountability.
What are the considerations for ensuring privacy in blockchain data-sharing?
Privacy-preserving techniques, such as pseudonymity and encryption, are used to protect sensitive data in blockchain data-sharing. Participants can maintain confidentiality while still benefiting from the transparency and security of the blockchain.
READ MORE:
Kibho Cryptocurrency: A Fine Choice for Huge Crypto Returns
Xxc Renegade 1000 Xxc Price Prediction: Will This ATV Gain Popularity In 2023?
YIMUSANFENDI: The Vanguard of Information-Driven Innovation
Yes Bank Share Price Prediction 2025: Will Yes Bank Stock Recover from Crisis?
AMC Stonk-O-Tracker: The Power of Retail Investors in the Market
How Can Features of Blockchain Support Sustainability Efforts
Controlling Bitcoin Mining Hashrate: Report on Core Scientific 545M & Riot Blockchain 215M Earning
Understanding the IEX Share Price on the National Stock Exchange
Reliance Power Share Price Future Prediction 2025: Will RPOWER Stock Reach ₹100 In 2023?























